Feedback Overview
Create new feedback for each problem (or solution) your product has, then use our toolset to organize and prioritize them against each other. Use your resources wisely by deeply understanding what your users need and how these needs align with the wider company goals.
Creating Feedback
You can create feedback either one at a time by going to Feedback and clicking the Create New Feedback button, or else by using the Bulk Import tool.
Organizing feedback
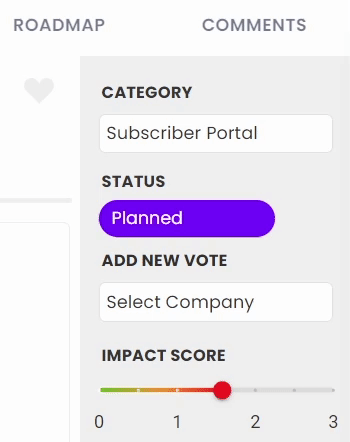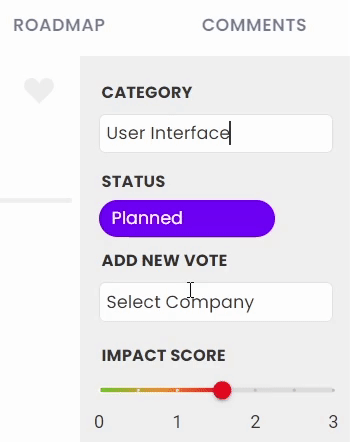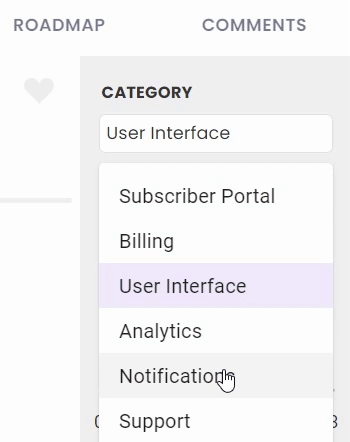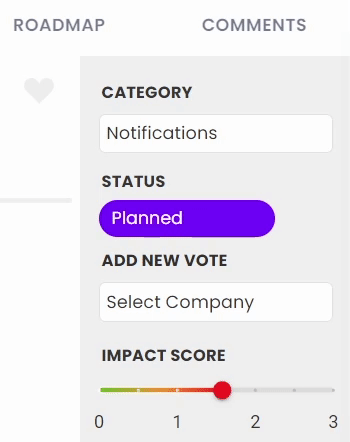
1. Category
Select a category your feedback fits into (after adding them from the navigation menu). This is a part of your company - maybe a specific product or part of the UI. Some examples are:
- Subscriber Portal
- Billing
- Support
- Notifications
2. Status
Change the status to match the current stage of development. The options are:
- To Triage. This is linked to the custom Triage Setting. New feedback will automatically be set to To Triage if this setting is enabled.
- Backlog. If the Triage Setting is not enabled, Backlog is the default for new feedback.
- Considering. When your team is considering building the feature - often a time when the feature is added to the public roadmap for feedback, and/or internal discovery is being done.
- Planned. A decision has been made to work on this feature - you may or may not also want to set an ETA when you change to this status.
- In Progress. When the feedback actively has a solution being worked on.
- Early Adopter. This is when the feature is in open/closed beta - you likely have a small group of users already using it.
- Complete. This is when the feature has been launched and is available to your customers.
- Not Planned. This status is to specifiy this is not a feature that will be built out. Having this allows greater transparency company-wide than just deleting the feature, and you can add a comment or update the feedback body to explain why.
- Blocked. This feature cannot be worked on until another feature (or similar) is complete. More information should be left in the feedback body or a comment.
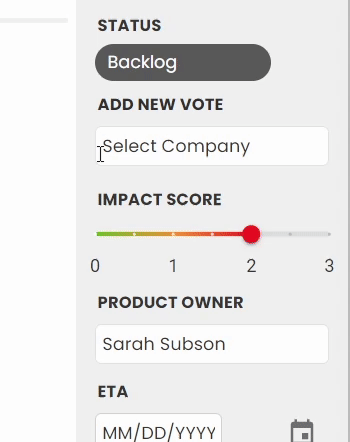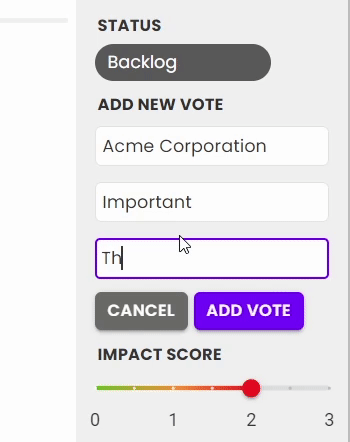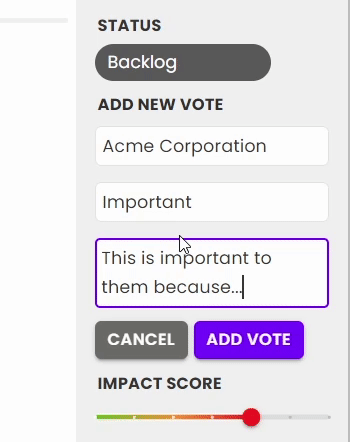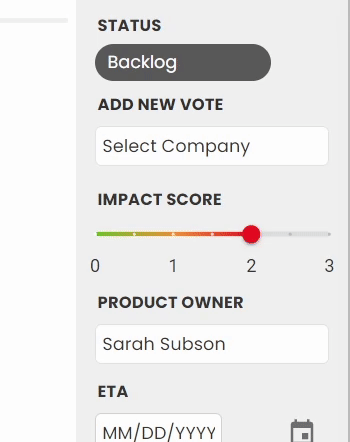
3. Votes and the impact score
Votes can come in through the roadmap, or added internally. You can learn more about how votes are added in our Votes and User Stories doc.
When new votes are added, you'll see the overall impact score updates - this is the average impact score across all votes. While some feedback will be highly requested, it may be less important to your customers than others. This allows another data point so that at a glance, you can see the highest priority feedback from your users.
4. MRR
MRR (monthly recurring revenue) is optionally available to add to each company as Monthly Spend. The MRR tied to a feature is the aggragated total of the monthly spends of all companies who have requested a feature.
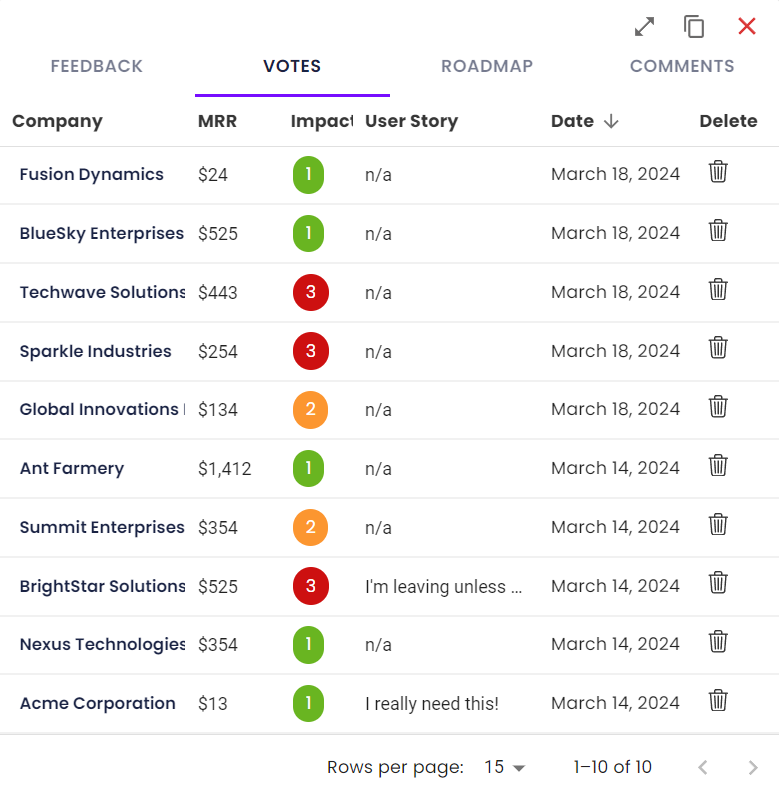
For example, if you have 20 votes on a piece of feedback and each of those companies pay you $50 a month, the MRR for that feature will be $1000. You may have another piece of feedback with only 8 votes, but higher-paying companies want it, and its MRR totals $10k.
This allows you to not just calculate value by number of votes, but by the value of those votes. Generally, users who pay more have more sway on future iterations to your product.
5. Product Owner
Assign a staff member to be the product owner for this feedback - this allows your internal teams to know who the point person is.
An additional bonus to assigning them is it allow the product owner to keep track of feedback related to their product. Their staff profile has a list of feedback assigned to them.
6. ETA
Share the planned release date! If the feedback is published to the roadmap, your public users will also see this date.
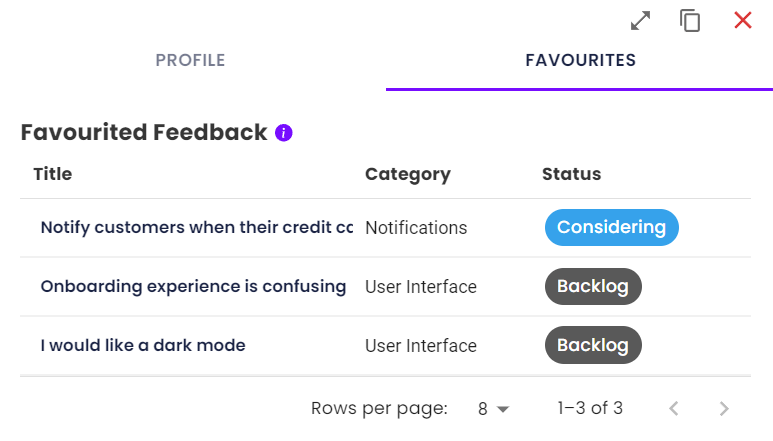
7. Favouriting
Sometimes internal teams have a special interest in specific features - this feature allows your logged in team members to favourite feedback. They can then access their favourites list in their staff profile.
8. Team 💎
After creating teams, you can then assign them to specific feedback. This helps keep track of the wider product team that is responsible for the feature.
9. Rice Score 💎
Use the popular RICE score method to determine a feature's priority. It calculates a numerical score based on Reach, Impact, Confidence and Effort - the higher number, the higher importance.
This feature can be disabled in Custom Settings.
10. OKR Alignment 💎
Track how closely certain feedback aligns with SLT priorities and company-wide OKRs.
In Custom Settings you can set up four OKRs relevant to your company. Then, move the sliders to show how much a piece of feedback aligns with these goals.
This feature can be disabled in Custom Settings.
11. Moscow Prioritization 💎
Use the popular Moscow rating as another prioritization option - choose between Must Have, Should Have, Could Have, Won't Have.
This feature can be disabled in Custom Settings.
